First study on mangabeira’s anti-inflammatory activity concludes it can be used to treat ulcers and similar disorders
10/03/2018 / By Michelle Simmons
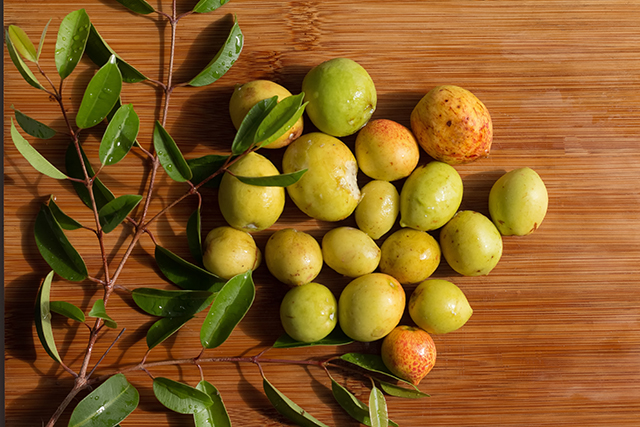

The fruits of the mangabeira (Hancornia speciosa Gomes) plant, a fruit plant species native to Brazil, have been used in traditional medicine for the treatment of ulcers, tuberculosis, and inflammatory disorders. In a study published in the journal BMC Complementary and Alternative Medicine, it was found that the fruit extract of mangabeira could be used to treat inflammatory problems.
For the study, researchers from the Federal University of Rio Grande do Norte in Brazil examined the anti-inflammatory properties and bioactive compounds of the aqueous extract of the fruits of mangabeira.
After producing an aqueous extract of the mangabeira fruits, they conducted a phytochemical analysis of the mangabeira fruit extract. Then, they assessed the extract and its bioactive compounds’ effect on inflammation. To do this, they gave the mangabeira aqueous fruit extract to mice models with xylol-induced ear edema, carrageenan-induced peritonitis, and zymosan-induced air pouch.
The phytochemical analysis revealed that the mangabeira fruit extract contains chlorogenic acid and rutin. The treatment with the mangabeira fruit aqueous extract of, as well as chlorogenic acid and rutin, substantially inhibited the xylol-induced ear edema. Cell migration in the carrageenan-induced peritonitis and zymosan-induced air pouch models were also reduced. In addition, the levels of cytokines were also reduced.
These findings indicate that the bioactive compounds chlorogenic acid and rutin may play an essential role in managing inflammation, contributing to the anti-inflammatory effect of mangabeira fruit extract.
Supplements that fight inflammation
Inflammation can occur as a result of trauma, illness, and stress. It can also be caused by unhealthy foods and lifestyle habits. Together with exercise, good sleep, and stress management, eating anti-inflammatory foods can help fight inflammation. (Related: 10 Anti-Inflammatory Foods for a Healthy Body.)
The following are some foods that help fight inflammation:
- Fatty fish, such as salmon, mackerel, tuna, and sardines
- Fruits, such as strawberries, blueberries, cherries, and oranges
- Green leafy vegetables, such as spinach, kale, and collards
- Nuts, such as almonds and walnuts
- Olive oil
- Tomatoes
Getting extra support from supplements may be helpful in some cases. Here are some anti-inflammatory supplements you can try:
- Alpha-lipoic acid – Alpha-lipoic acid, a fatty acid produced by the body, is essential in metabolism and energy production. It is also an antioxidant, which means that it can reduce inflammation and may improve symptoms of certain diseases. The recommended dosage for alpha-lipoic acid supplements is 300 to 600 milligrams (mg) each day.
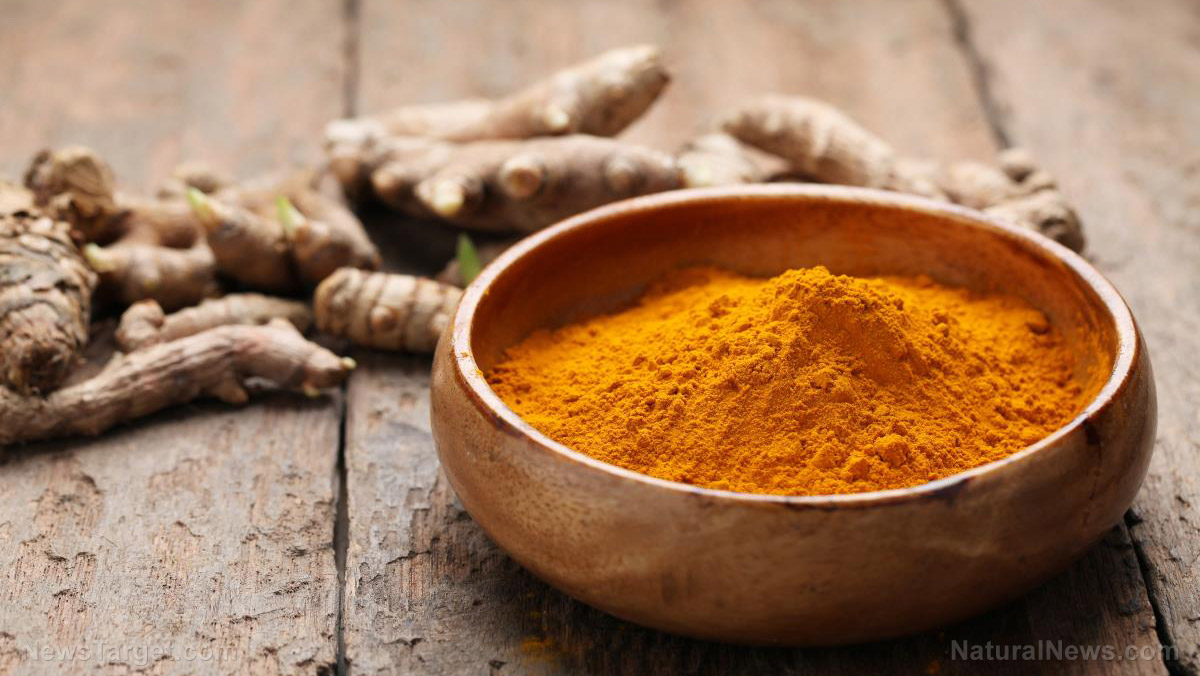
- Curcumin – A component of turmeric, curcumin can reduce inflammation in many diseases, such as diabetes, heart disease, inflammatory bowel disease, and cancer. The recommended dosage for curcumin is 100 to 500 mg daily when taken with piperine.
- Fish oil – Fish oil supplements contain omega-3 fatty acids which can reduce inflammation associated with various diseases, such as diabetes, heart disease, and cancer. The recommended dosage for fish oil supplements is 1 to 1.5 grams daily.
- Ginger – Ginger supplements contain gingerol and zingerone, which may decrease the inflammation associated with colitis, kidney damage, diabetes, and breast cancer. It can also reduce muscle pain and soreness after exercise. The recommended dosage for ginger supplements is one gram daily.
- Resveratrol – Resveratrol, an antioxidant, is found in red wine, peanuts, grapes, blueberries, and other purple-colored fruits. Resveratrol supplements may decrease several inflammatory markers in people with heart disease, insulin resistance, gastritis, and ulcerative colitis. The recommended dosage for resveratrol supplements is 150 to 500 mg daily.
- Spirulina – A type of blue-green algae, spirulina contains powerful antioxidant properties. Its antioxidant content can reduce inflammation and may improve symptoms of certain diseases. Supplementation with spirulina may also result in healthier aging and may boost the immune system. The recommended dosage for spirulina is one to eight grams per day.
Read more news stories and studies on healing foods like mangabeira by going to Fruits.news.
Sources include:
Tagged Under: alternative medicine, anti-inflammatory, fruits, Hancornia speciosa Gomes, herbal medicine, Herbs, inflammation, mangabeira, natural cures, natural medicine